How an AI gateway improves AI app building
See how how an AI gateway improve building AI apps acting as a control layer between AI apps and model providers for routing, governance, and observability.
Building an AI app has become deceptively easy. A few lines of code, an API key, and a model endpoint are often enough to get a working prototype.
The difficulty shows up once that prototype starts behaving like a real product.
As soon as an AI app is exposed to real users, teams begin dealing with issues that aren’t obvious at demo time.
On top of that, most teams don’t build just one AI app. They build multiple internal tools, experiments, and production systems, often across different teams and environments. Each app ends up managing its own model access, retry logic, budgets, and logging. Over time, this creates duplication, blind spots, and operational risk.
This is the gap between getting an AI app to work and operating AI apps reliably at scale. An AI gateway exists to close that gap.
What an AI gateway does in an application architecture
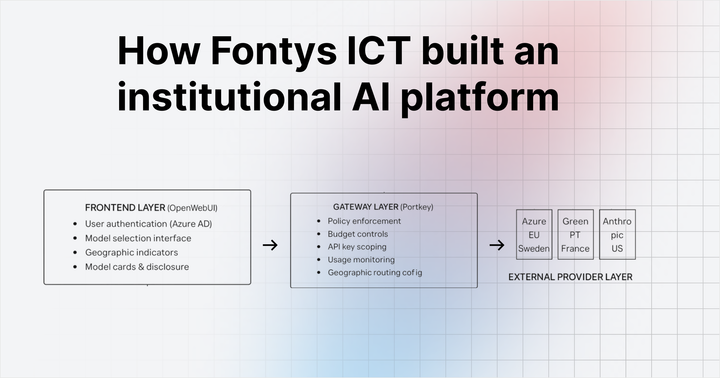
An AI gateway sits between your applications and the AI model providers they depend on.
Instead of each application talking directly to OpenAI, Anthropic, Gemini, or other providers, all requests flow through a single gateway layer. This layer becomes the shared entry point for model access, policies, and telemetry.
From an architectural standpoint, the gateway does not replace application logic or agent frameworks. It abstracts provider-specific details and handles cross-cutting concerns that every AI app eventually needs, such as authentication, routing, retries, logging, and enforcement of organizational rules.
This separation is important. Application teams focus on prompts, workflows, and user experience. Platform teams define how models can be accessed, monitored, and controlled across the organization. The gateway becomes the boundary between the two.
Over time, this pattern reduces tight coupling between apps and providers. Switching models, adding new providers, or introducing controls no longer requires touching every codebase. Those changes happen once, at the gateway layer, and apply consistently across all AI apps.
Simplifies model access across providers
Most AI apps start with a single model provider. Over time, that rarely stays true.
Teams add new providers to improve quality, reduce latency in specific regions, or control cost. Without an abstraction layer, this means integrating multiple SDKs, handling different request formats, and managing provider-specific edge cases in application code.
An AI gateway simplifies this by presenting a unified interface for model access. Applications make the same type of request regardless of which provider or model is used underneath. Provider differences are handled once, centrally, instead of repeatedly across apps.
This has a direct impact on developer velocity. Teams can experiment with different models without rewriting large parts of their code. Switching from one provider to another becomes a configuration change rather than a refactor. New models can be introduced gradually, without disrupting existing workflows.
For organizations building multiple AI apps, this consistency matters. It reduces cognitive overhead for developers and prevents each team from solving the same integration problems in slightly different ways.
Improves reliability for production workloads
Reliability becomes a concern the moment an AI app moves into production. Model APIs can return errors, slow down under load, or behave inconsistently across regions. When each application handles these failures on its own, reliability depends heavily on how carefully that logic was implemented.
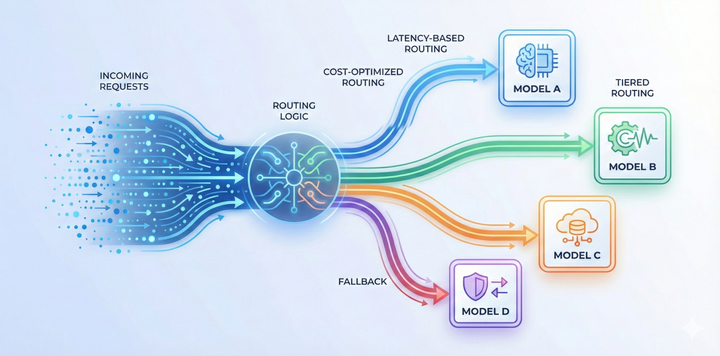
An AI gateway centralizes reliability strategies instead of pushing them into every codebase.
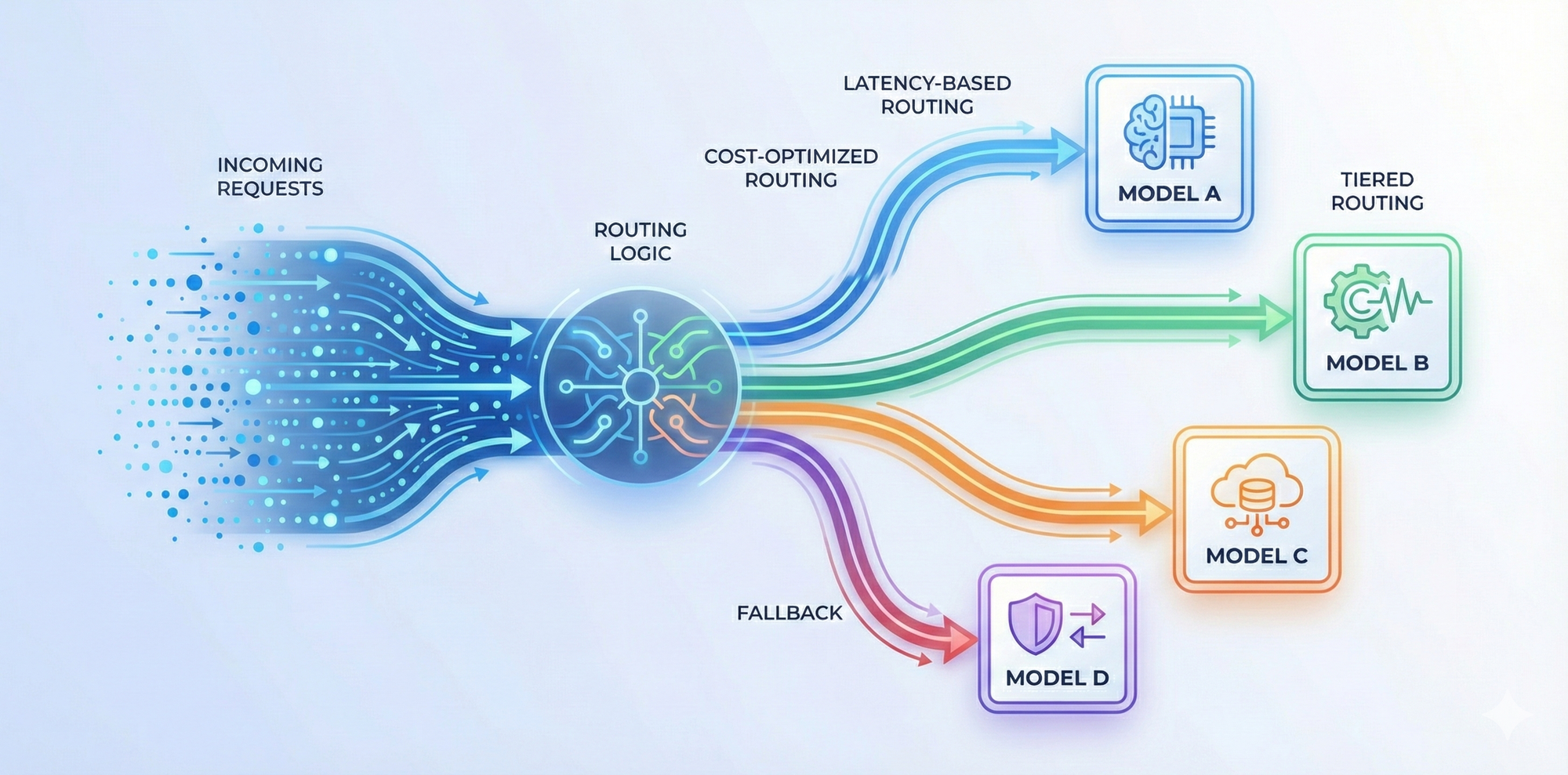
Requests can be routed dynamically based on availability, latency, or predefined rules. If a provider degrades or becomes unavailable, traffic can fall back to an alternative model without breaking the application. Load can be spread across targets in a controlled way, reducing the impact of sudden spikes.
For multi-step or session-based workflows, consistent routing also matters. When requests that belong together are handled predictably, debugging becomes easier and application behavior is more stable.
The result is not just fewer outages. It’s a system where failures are expected, handled gracefully, and resolved in one place rather than rediscovered by each team independently.
Adds control without slowing teams down
As LLM usage spreads across an organization, control becomes unavoidable. Different teams have different requirements around data handling, compliance, and risk. Without a shared control layer, those requirements are enforced inconsistently, or not at all.
An AI gateway provides a way to apply controls centrally, without pushing friction into every application.
Access rules can be defined once and applied across environments, teams, or workloads. Guardrails help ensure that sensitive data is handled appropriately and that only approved models are used for regulated use cases. At the same time, teams building internal tools or experiments are not blocked by heavyweight review processes.
This balance is important. Too little control leads to risk and sprawl. Too much control slows delivery and encourages workarounds. By placing AI governance at the gateway layer, organizations can set clear boundaries while allowing application teams to move quickly within them.
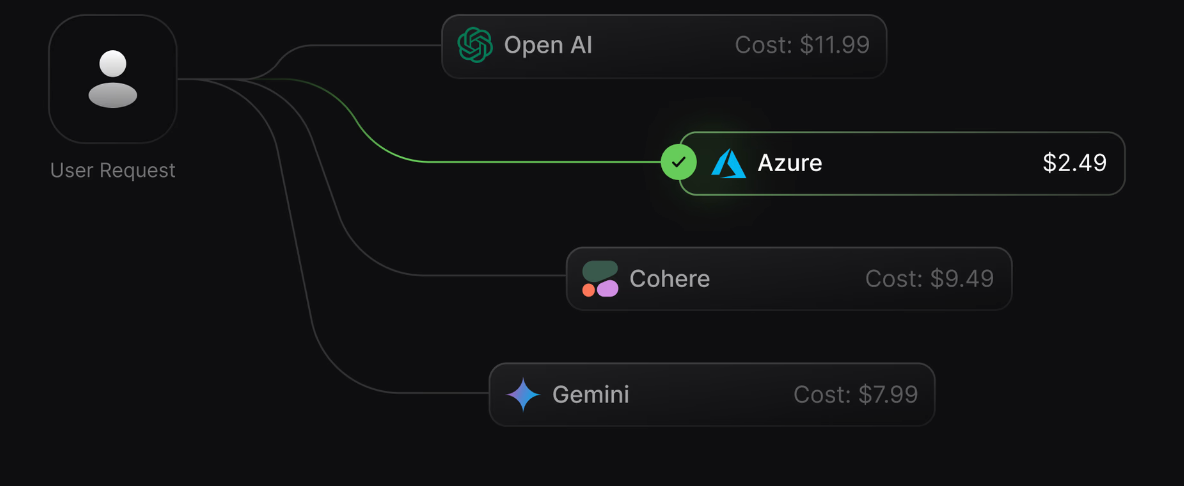
Makes cost predictable as usage grows
Cost is often the first scaling problem teams feel with AI apps.
Usage grows unevenly. A feature that works fine in testing can generate millions of tokens once it reaches real users. Different models price tokens differently, and small changes in prompts or output length can have a large financial impact over time.
An AI gateway introduces a single place to observe and control this behavior.
Because all requests pass through the gateway, teams can see how tokens are being consumed across applications, users, and environments. Budgets and rate limits can be applied centrally, preventing runaway usage before it becomes a billing surprise. Models that are appropriate for experimentation can be restricted from high-volume paths, while production workloads can be tuned for cost efficiency.
This shifts cost management from reactive cleanup to proactive design. Teams can make informed trade-offs and maintain balance quality, latency, and spend, without embedding cost logic into every application.
Improves observability across AI interactions
When something goes wrong in an AI app, the root cause is often hard to pinpoint. Was it the prompt, the model, the provider, or the way the request was routed? Without centralized LLM observability, answers are scattered across logs that may not even exist.
An AI gateway becomes a shared observability layer for all AI interactions.
Because every request flows through the LLM gateway, prompts, responses, metadata, latency, and errors can be captured in one place, subject to organizational policies. This makes it possible to trace behavior across providers and workloads without stitching together logs from multiple systems.
For debugging, this shortens feedback loops. Teams can see how a change in prompts or routing affects output quality and performance. For audits and reviews, there is a consistent record of how models are being used and by whom.
Over time, this visibility turns AI systems from opaque services into components that can be measured, reasoned about, and improved systematically.
Enables faster iteration on AI product behavior
AI product development does not stop once an app ships. Prompts evolve, models improve, and usage patterns change as users interact with the system in unexpected ways.
Without an AI gateway, many of these changes require application code updates and redeployments. That slows iteration and increases risk, especially for teams supporting multiple apps.
An AI gateway allows teams to adjust behavior at the infrastructure layer. Routing rules can be updated to test new models. Caching, retries, and other request-level behaviors can be tuned without touching application logic.
This separation makes experimentation safer. Teams can run controlled tests, compare outcomes, and roll back changes quickly if needed. Product teams move faster, while platform teams maintain consistency across the system.
When an AI gateway becomes necessary, not optional
Not every AI project needs an AI gateway on day one. For small experiments or single-user tools, direct provider integration can be sufficient.
The need for a gateway becomes clear as systems mature.
This typically happens when teams move from one AI app to many, or from internal use to customer-facing workloads. Multiple providers enter the stack. Costs become material. Reliability expectations increase. Platform and security teams need visibility and control that individual apps cannot easily provide on their own.
At this stage, the question is no longer whether a gateway adds value, but where these shared concerns should live. Embedding them into every application creates inconsistency and operational debt. Centralizing them at the gateway layer creates leverage.
An AI gateway marks the transition from experimenting with AI to operating it as a platform capability.
How does Portkey's AI gateway improve building AI apps
Portkey's AI gateway is designed for teams that are building and operating AI apps at scale.
It provides a single gateway for accessing models across providers, with built-in routing, reliability controls, and observability. Platform teams can define guardrails, budgets, and access policies centrally, while application teams continue to focus on product logic and user experience.

Because these capabilities live at the gateway layer, changes do not require repeated updates across codebases. Teams get consistent behavior across environments, clearer insight into usage and cost, and a more reliable foundation for production AI systems.
If you’re moving beyond experiments and starting to treat AI as a core platform capability, an AI gateway like Portkey helps make that transition manageable.
Explore how Portkey supports production AI apps across teams and workloads.