LLM hallucinations in production
Hallucinations in LLM applications increase at scale. This blog explains how AI gateways and guardrails help control, detect, and contain hallucinations in production systems.

LLM hallucinations are often framed as a model limitation. But they surface as a system reliability issue.
In early demos, hallucinations feel rare and manageable. In production, they show up differently: confident but incorrect answers, fabricated explanations, invented references, or tools being used in unintended ways. As usage scales across teams, workflows, and applications, these failures become harder to predict and harder to contain.
What LLM hallucinations actually are
Hallucinations occur when a model generates outputs that are syntactically valid and semantically plausible, but factually incorrect or ungrounded.
For production systems, the most important framing is: the model generated something that is not grounded in the information it was supposed to use (for example, your retrieved documents, tool outputs, or explicit system constraints). Research often distinguishes between “intrinsic” and “extrinsic” hallucinations; for most enterprise apps, extrinsic grounding failures are the ones that turn into incidents.
In practice, hallucinations tend to fall into a few common buckets:
- Factual hallucinations: The model invents facts, entities, or explanations that do not exist.
- Reasoning hallucinations: The output is coherent, but it contains contradictions, invalid assumptions, or conclusions that do not follow from the provided evidence.
- Tool and action hallucinations: The model calls tools incorrectly, fabricates parameters, or attempts actions outside its allowed scope (sometimes with high confidence).
What makes hallucinations dangerous is not their frequency, but the confidence and fluency of the hallucinating model. These makes the outputs look trustworthy, making them difficult to detect without explicit controls.
Teams sometimes rely on an AI detector as part of their evaluation and monitoring stack to flag outputs that appear coherent but are likely ungrounded, inconsistent with source material, or outside expected behavioral boundaries.
Why hallucinations increase in real applications
Hallucinations are amplified by the realities of production usage.
Real systems introduce variability that demos do not - user inputs are unpredictable, Prompts grow longer, Requests vary in intent, sensitivity, and complexity - and applications move beyond single-turn interactions into workflows and agents that reason, retry, and chain actions.
As systems scale, teams also introduce:
- Multiple models for different tasks
- Cost or latency driven routing decisions
- Tool calling and external integrations
- Shared infrastructure across teams and environments
Each layer increases the chance that a model will operate outside the assumptions it was originally tested under. Without system level controls, hallucinations become harder to trace and harder to prevent.
Why model upgrades alone don’t solve hallucinations
Newer models reduce hallucination rates, but they do not eliminate them.
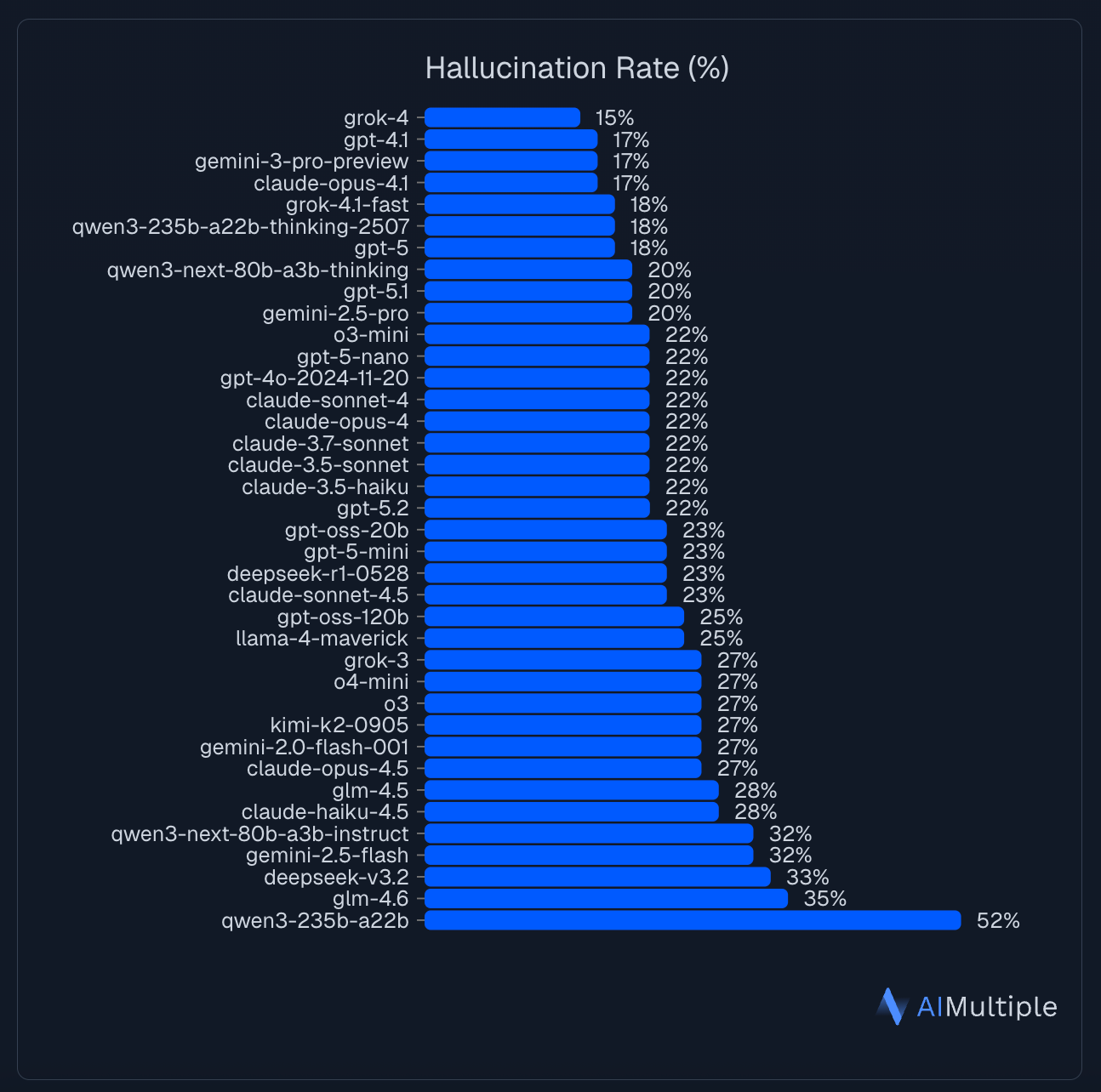
Even the latest models have >15% hallucination rates when they are asked to analyze provided statements. (Source)
More importantly, improvements at the model level do not address failures introduced by orchestration decisions. A routing change, a fallback model, or a new tool integration can reintroduce hallucination risks even when using strong base models.
In production, reliability is no longer a single-model concern. It is a property of the entire AI stack.
Treating hallucinations as something that will be “fixed by the next model” delays the real work: building systems that expect failures and contain them.
The role of an AI gateway in reducing hallucinations
LLM hallucinations do not emerge in isolation. They surface when models are used inconsistently, routed unpredictably, or allowed to operate without clear boundaries. An AI gateway addresses these risks by introducing a central control layer between applications and models.
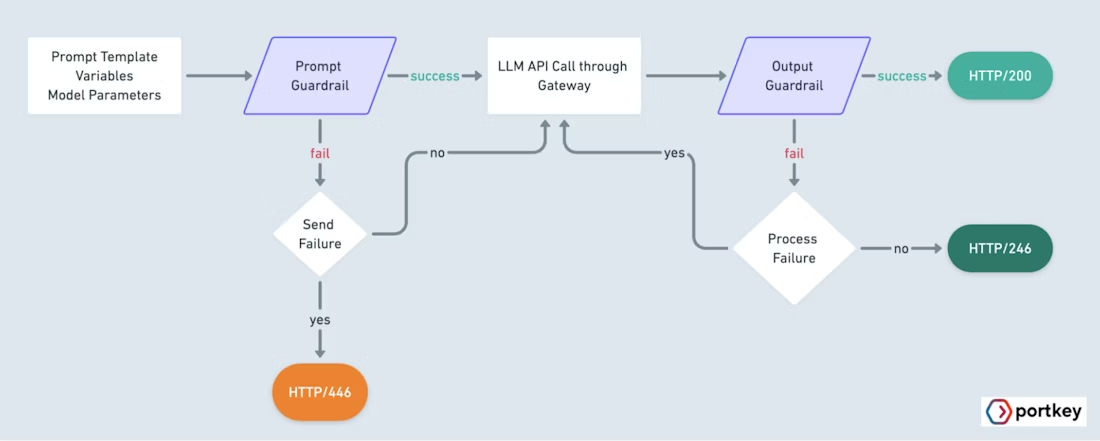
Rather than attempting to “fix” hallucinations at the output level, the gateway reduces the conditions that cause them to occur and propagate across systems. Additionally, It enables adding a layer that validates correctness and enforces semantic boundaries on AI outputs.
Enforcing consistency at the request level
In large organizations, hallucinations often appear when each team constructs prompts differently or modifies system instructions over time.
An AI gateway enforces consistency by applying constraints across applications and environments.
This reduces unintended behavioral changes that can trigger hallucinations, especially as teams scale or rotate ownership.
Making model selection an explicit decision
Different models exhibit different hallucination patterns. Without a central layer, routing decisions are often hidden inside application code and evolve informally.
An AI gateway makes routing explicit:
- Models can be selected based on task risk, not just cost or latency
- Sensitive workloads can be isolated from experimental traffic
- Fallback behavior becomes intentional instead of implicit
This limits the blast radius when routing changes introduce new failure modes.
Constraining tool usage and side effects
When models are allowed to call tools, hallucinations can translate into real actions.
A gateway defines clear boundaries:
- Which tools are available for a request
- Which actions are allowed or forbidden
- When tool usage must be blocked entirely
Adding contextual guardrails, allows validating the intent behind invoking a tool. Even if the agent is allowed to send emails, the model might hallucinate a reason or user intent, which can be prevented by having the right guardrails in place
By narrowing the model’s action surface, the gateway and integrated guardrails prevent exploratory or fabricated tool calls from causing downstream impact.
Turning hallucinations into observable signals
Hallucinations are difficult to address when they appear as isolated incidents.
An AI gateway centralizes visibility into:
- Prompts and responses across applications
- Routing and fallback decisions
- Patterns tied to specific models or workflows
This allows teams to treat hallucinations as debuggable system behavior, not anecdotal failures. Continuous evaluation at runtime will detect and flag hallucination suspects, providing valuable observability into the system's coherence and reliability.
Enforcing output expectations downstream with guardrails
Once you have centralized routing and telemetry, the next step is turning those traces into decisions. This is where guardrails fits: it continuously evaluates real production interactions for grounding and consistency, so teams can spot emerging hallucination patterns early, quantify the risk by workflow and model, and decide where to enforce stricter policies. Instead of treating hallucinations as isolated incidents, you get a feedback loop that connects what happened in production to what gets changed upstream (prompts, retrieval, routing, and tool policies).
This ensures that hallucinations do not silently reach users or trigger unintended actions.
Why guardrails are essential alongside an AI gateway
An AI gateway controls how models are used.Guardrails control what inputs and outputs are acceptable.
Gateways reduce exposure to hallucinations, but they do not validate outputs. In production systems, outputs must still be checked, verified, and enforced against explicit rules.
This is where guardrails become essential. They provide the enforcement layer that determines whether a response can be trusted, modified, blocked, or escalated.
The combination matters: without a gateway, guardrails lack system context. Without guardrails, gateways lack output enforcement.
In production, hallucinations are the unknown unknowns. You cannot regex hallucinations, and you cannot statically test for them - hallucinations will surprise you at runtime in the most creative ways.
Grounding and consistency checks are the best way to detect and mitigate extrinsic hallucinations. Production grade guardrails are powered by small language models that enables semantic checks, while maintaining the latency low. It enables teams to test agentic workflows before deployment, continuously evaluate model behavior as prompts and tools evolve and block hallucinated, unsafe or non compliant outputs before they reach users.