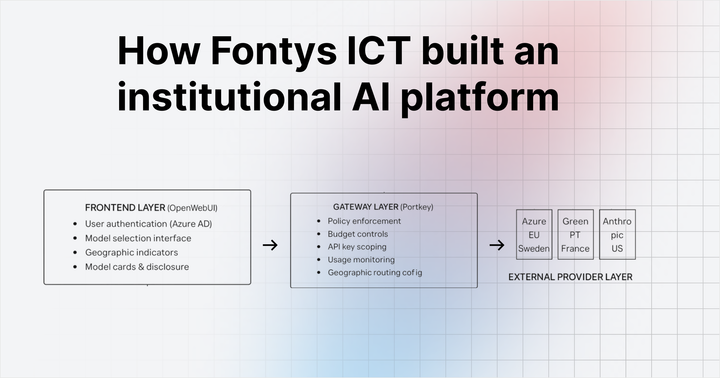
What is an LLM Gateway?
Understand how LLM Gateways help organizations run LLMs as shared infrastructure with consistent governance, security, and observability.
Over the last few years, LLMs have moved from experimentation to default infrastructure. They now sit behind internal copilots, customer-facing workflows, developer tools, and data systems across most AI-driven organizations.
The shift happened quickly, but the operating model hasn’t caught up.
Most teams still interact with LLMs as if they were isolated APIs: model-specific integrations, hardcoded routing logic, ad hoc retries, and fragmented monitoring. That approach works at small scale, but it breaks down once LLM usage becomes shared, continuous, and business-critical.
In this post, we’ll look at why LLM Gateways have emerged, what problems they solve in production systems, and how they simplify running LLMs at scale.
Check this out!
Why do LLMs need a gateway?
When teams first adopt LLMs, direct integrations work well enough. A single model, a single provider, a small number of use cases, manual decisions and hardcoded logic are manageable.
That changes quickly.
Once LLM usage spreads across teams and workflows, organizations start encountering operational bottlenecks.
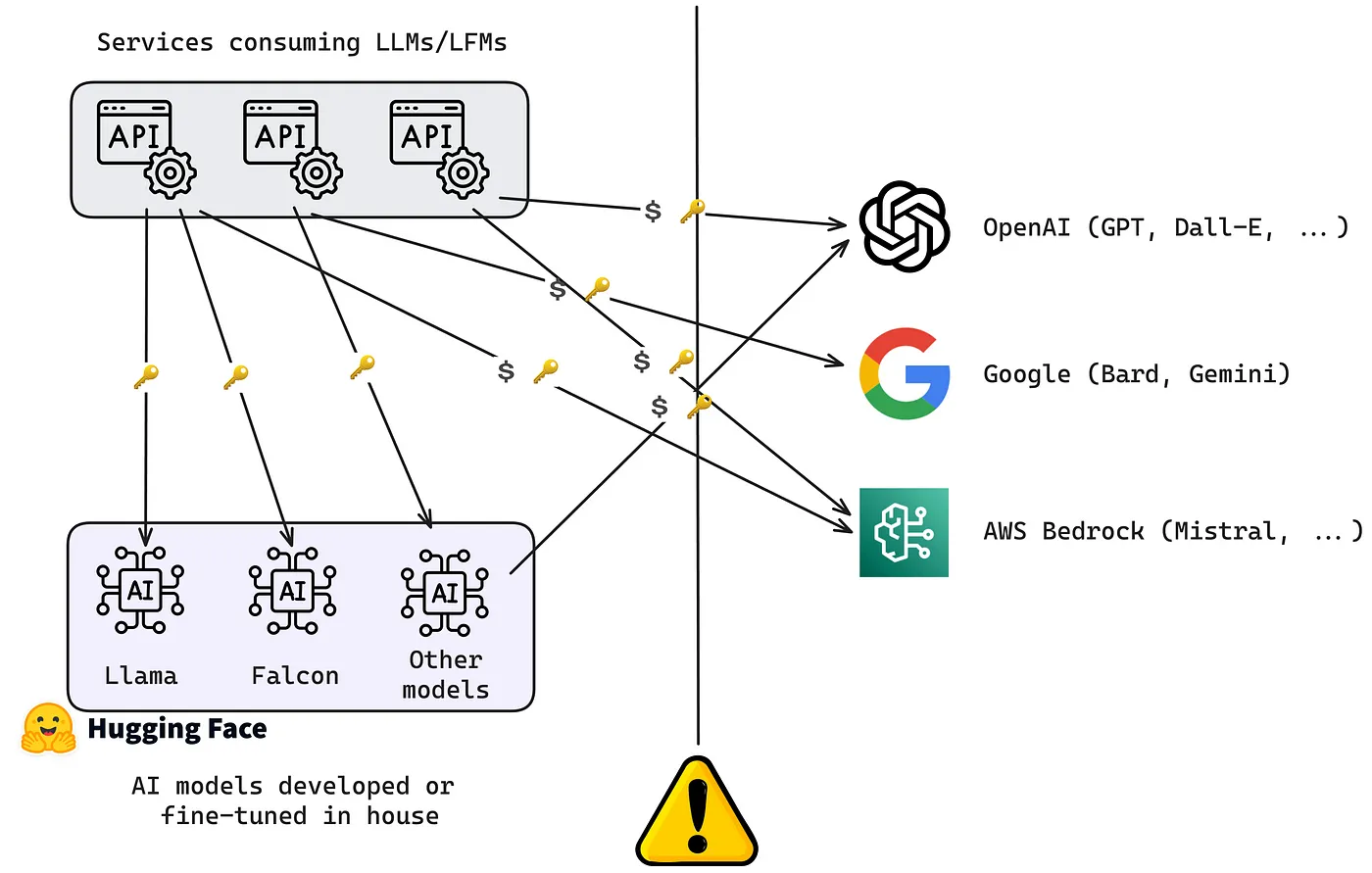
- Different APIs: Every LLM provider has its own API with unique rules, formats, and limits. This makes it harder to connect multiple models to a single application without custom coding for each one.
- Choosing the Right Model: Not all LLMs are good at every task. Picking the best model for a specific job, while keeping costs, speed, and accuracy in mind, can be tricky without an automated system.
- Managing Resources: LLM spend scales non-linearly with usage. Without centralized visibility and enforcement, costs are often discovered retroactively, after budgets have already been exceeded.
- Tracking Performance: Debugging and monitoring models can be tough when they’re spread across multiple systems. Developers need clear tools to track how models are performing, identify errors, and fix issues quickly.
- Ensuring Security: LLMs often handle sensitive information, so it’s important to have safeguards in place to protect data and ensure the outputs meet privacy and compliance standards.
- Scaling for Growth: As LLMs power critical workflows, downtime and degradation become unacceptable. Provider outages, rate limits, and transient failures are inevitable. Handling these gracefully is difficult to do consistently when logic lives inside application code.
What is an LLM Gateway?
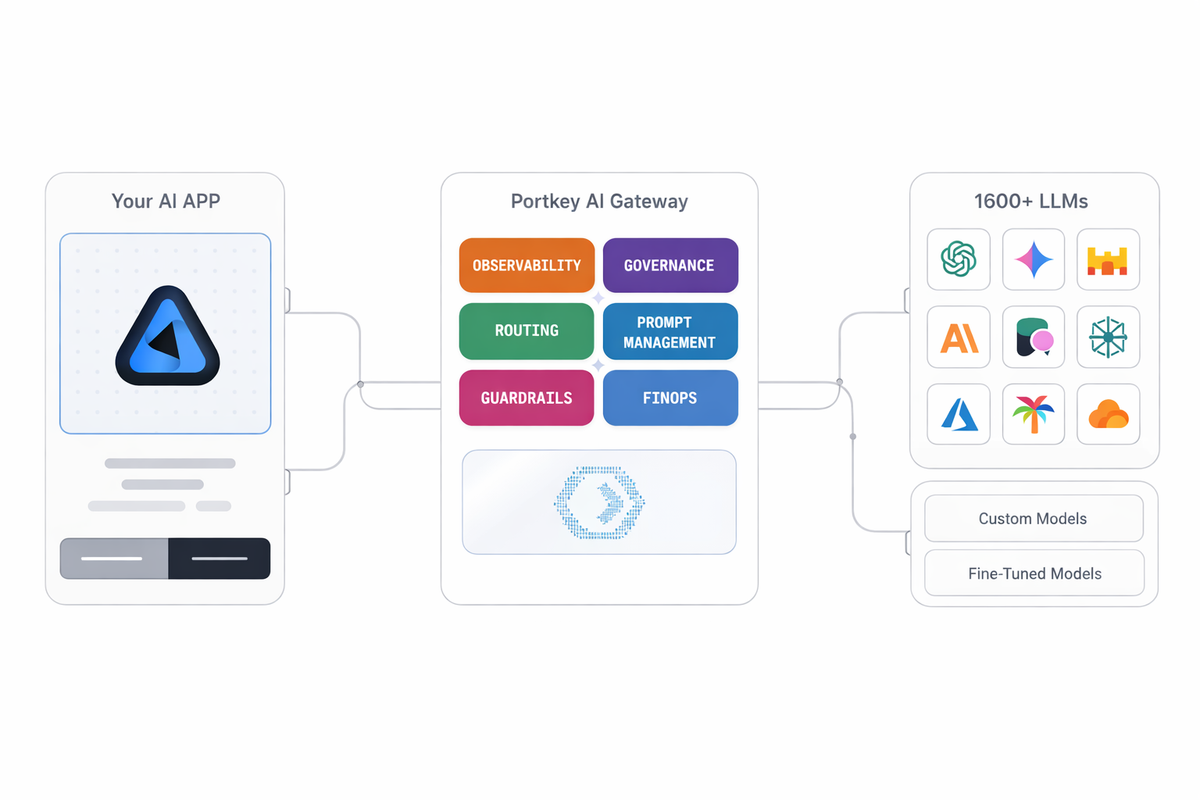
The LLM Gateway is a centralized control plane that sits between applications and the LLMs.
Instead of applications interacting directly with individual LLM APIs, all traffic flows through the gateway. This allows organizations to standardize how models are accessed, governed, and operated—without coupling application logic to specific providers or models.
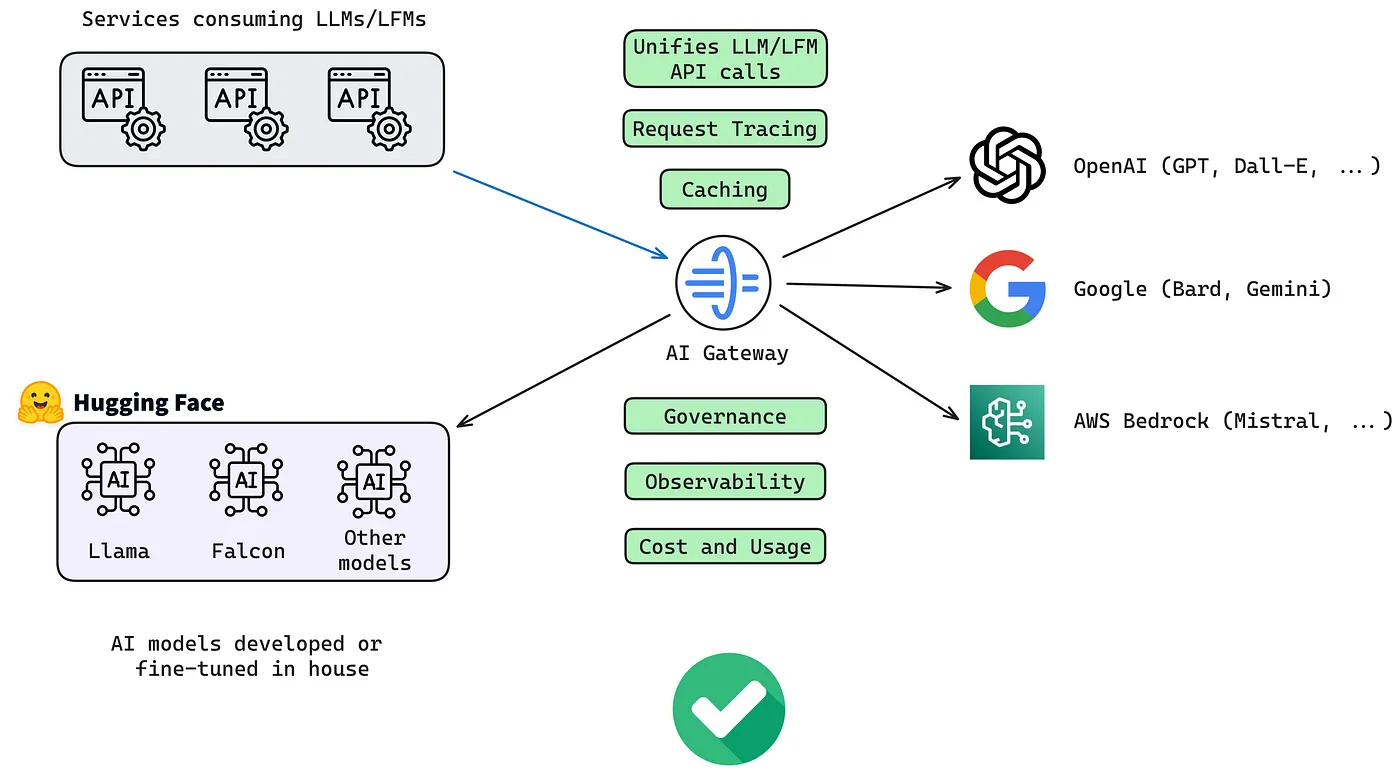
Core Functions of an LLM Gateway
- Request standardization and orchestration:
LLM requests vary widely across providers, input formats, parameters, token handling, and response structures all differ.
The gateway standardizes this at the boundary:
- Normalizes inputs into a consistent format
- Applies request-level validation and preprocessing
- Translates requests into provider-specific formats
Because the gateway is decoupled, your AI apps and agents are insulated from model churn, provider API changes, pricing updates, and evolving governance, allowing LLM usage to scale without constant rewrites.
- AI Governance:
An LLM Gateway acts as the enforcement point for organizational AI policies, including:
- who can access which models and capabilities
- which applications or teams can generate which types of outputs
- how sensitive data is handled across inputs and responses
- where requests are allowed to run (region, residency, deployment boundary)
- Monitoring and Observability:
With the gateway you get, request-level logs and traces, latency metrics, usage data and cost tracking. This enables debugging, performance tuning, and continuous improvement.
- Performance Optimization:
Routing decisions shift from static configuration to runtime policy. You can set up configs to selects models based on:
- latency and performance targets
- model capabilities
- availability and health signals
Routing allows teams to rebalance traffic, introduce new models, or respond to outages without code changes.
- Reliability
As LLMs become part of critical application paths, reliability can’t be treated as an edge case. An LLM Gateway centralizes failure handling through retries, fallbacks, load balancing, and circuit breaking, shielding applications from provider outages, rate limits, and transient degradation.
By absorbing failures at the platform level, the gateway ensures consistent behavior and predictable performance, even when underlying models or providers are unstable.
- Cost controls
LLM costs scale dynamically with usage, making post-hoc reporting insufficient for production systems. An LLM Gateway enforces cost controls directly in the request path by tracking spend at a granular level, applying budgets and rate limits, and optimizing usage through caching and batching.
- Security and Compliance:
An LLM Gateway enforces guardrails and policy controls across all LLM interactions. It also supports regulatory compliance, such as GDPR and SOC 2, by centralizing auditability, access control, and data governance.
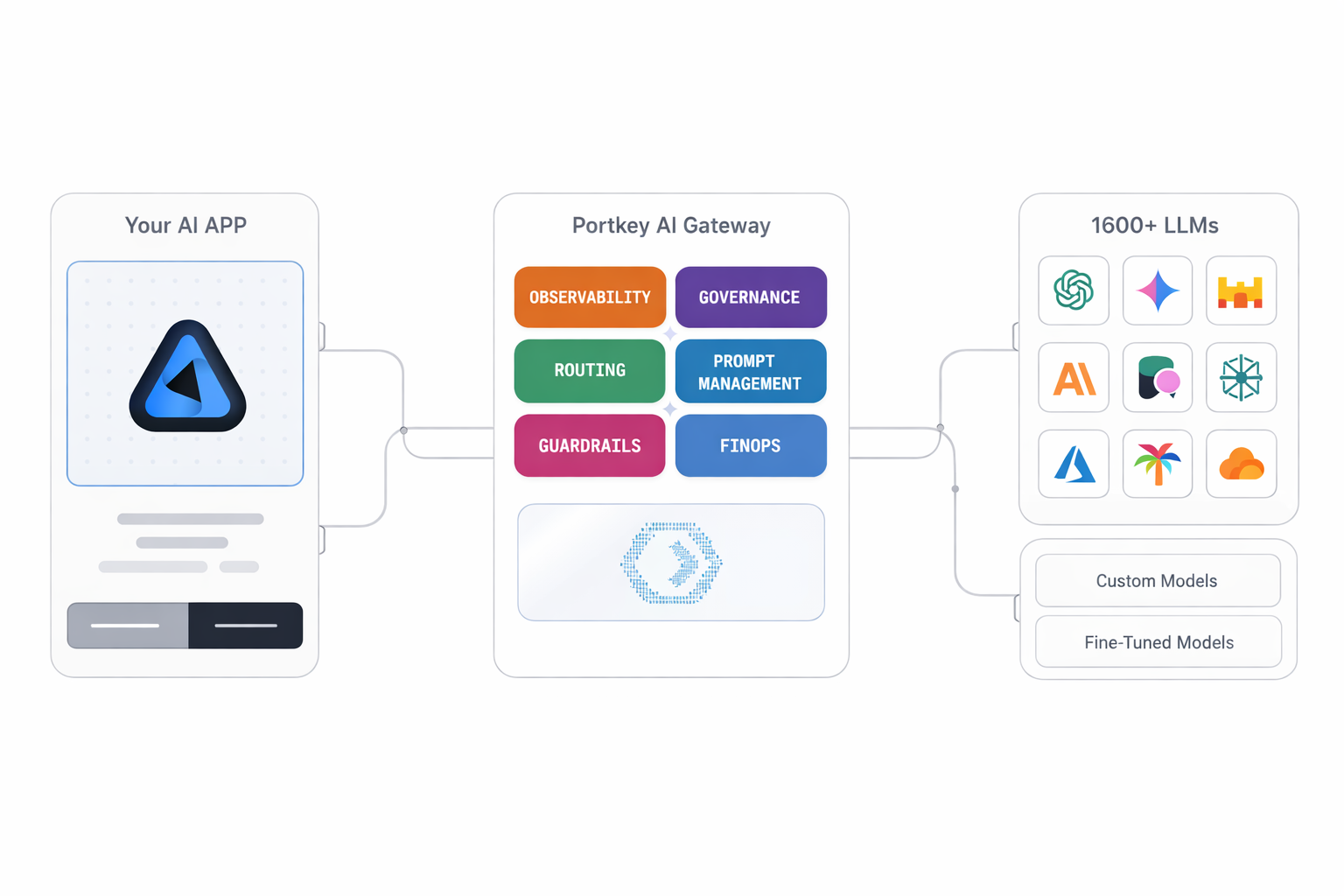
How does an LLM Gateway work?
Here's a breakdown of how it works, step by step:
1. Request handling
When an application sends a query or task, the LLM Gateway acts as the first point of contact. It parses the input, validates it for completeness and compliance (e.g., ensuring no sensitive data is included), and prepares it for processing. This ensures the system handles only valid and secure data.
2. Routing
The gateway evaluates the incoming request and determines which LLM is best suited for the task. Factors like model capabilities, cost efficiency, latency, and accuracy are considered.
3. Real-Time guardrails
As the request is processed, real-time AI guardrails come into play to enforce compliance and ethical standards. These safeguards ensure that the output avoids: - harmful or biased content.
- meets regulatory and organizational requirements (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- aligns with predefined business rules, such as maintaining a specific tone or avoiding sensitive information leakage.
Guardrails can also include tools like filters, PII redaction, or even reinforcement models that adjust outputs on the fly.
4. Integration and transformation
Once the LLM generates a response, the gateway can format, transform, or augment the output as needed, ensuring it aligns with the application's requirements.
5. Observability and feedback
Throughout the process, the gateway continuously monitors performance through observability tools. It generates real-time logs, metrics, and analytics to track latency, errors, and resource usage.
6. Output delivery
Finally, the processed response is delivered back to the application. This smooth flow ensures the application receives high-quality, contextually relevant outputs with minimal latency.
Why Portkey’s LLM Gateway stands out
Lightweight to start, robust in production
Portkey is designed to be easy to adopt. Teams can get started without re-architecting their systems or locking into a complex setup. At the same time, it’s proven at scale, processing 50 billion tokens every day in production environments.

Secure by design
Security and compliance are built into the gateway, not layered on later. Portkey aligns with enterprise requirements including SOC 2, GDPR, AICPA, and ISO 27001, allowing teams to run LLM workloads while meeting internal security standards and external regulatory obligations.
Flexible deployment, on your terms
Teams can run it fully managed, operate in hybrid setups, or support air-gapped environments where required. This flexibility allows organizations to adopt LLM infrastructure without compromising on data residency, network boundaries, or operational preferences.
Open-source at its core
The LLM Gateway is open source, with a growing community of contributors and over ten thousand GitHub stars. This openness provides transparency into how the gateway works, encourages ecosystem adoption, and ensures teams are not locked into a black-box system for critical AI infrastructure.
Built with a partner ecosystem
Portkey integrates with a broader ecosystem of providers and partners across models, guardrails, observability, and tooling. This allows teams to compose their AI stack intentionally, while using the gateway as the unifying control layer.
LLM Gateway for production AI
LLMs have already crossed the adoption threshold. The challenge now is no longer access to models, but operating them reliably as shared infrastructure across teams, applications, and environments.
The long-term value of an LLM Gateway is in reducing coordination cost: enabling teams to scale LLM usage, introduce new models, and enforce policies without repeated rewrites or fragmented controls.
If you’re running LLMs in production and want a centralized way to manage routing, governance, reliability, and compliance, explore Portkey’s LLM Gateway.
You can get started quickly, or reach out to us for a quick demo.