MCP Message Types: Complete MCP JSON-RPC Reference Guide
This guide provides a complete reference for every MCP message type, with real JSON examples you can use in your implementations.
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) uses JSON-RPC 2.0 for all communication between clients and servers. Whether you're building an MCP server, debugging a connection issue, or integrating with an AI assistant, understanding these message types is essential.
This guide provides a complete reference for every MCP message type, with real JSON examples you can use in your implementations.
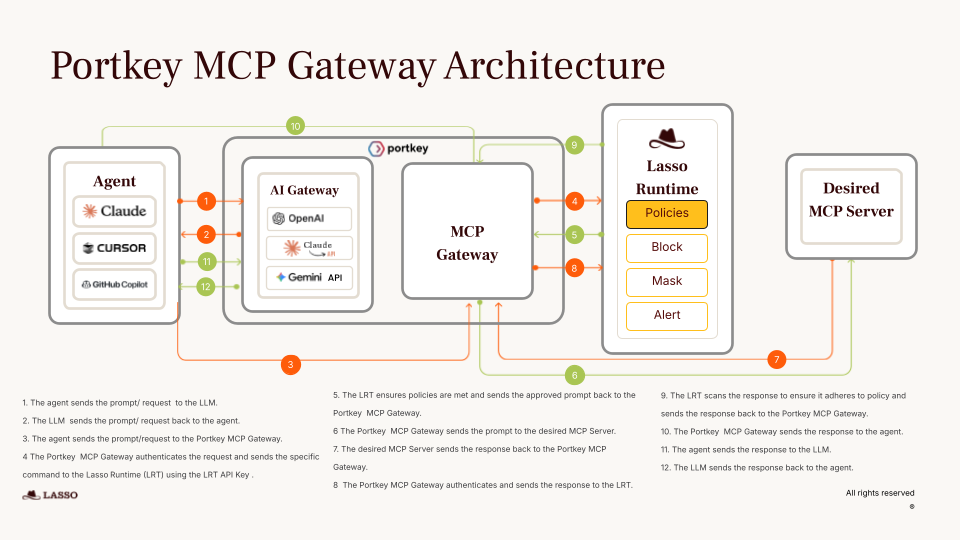
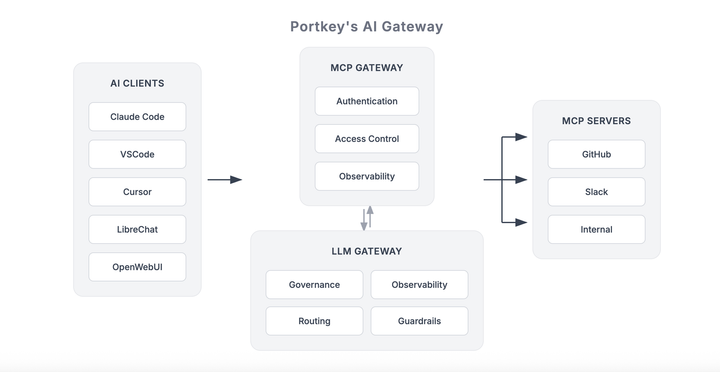
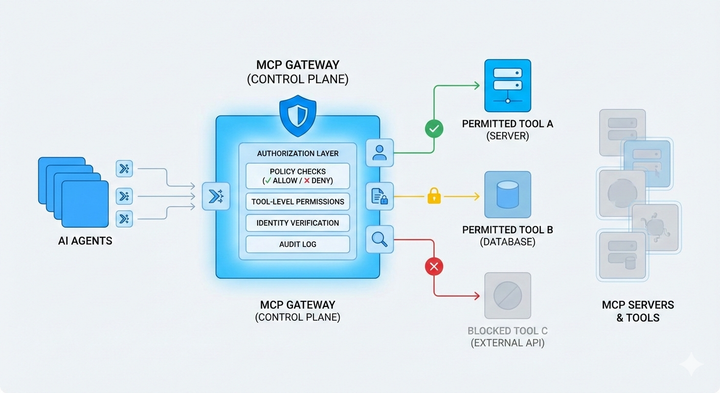
That’s why we built the MCP Gateway: a centralized control layer to run MCP-powered agents in production.
Check it out!
Quick Reference Table
Before diving into examples, here's every MCP message type in JSON-RPC format at a glance:
Client → Server Requests
| Method | Schema Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
initialize |
InitializeRequestSchema |
Establish connection and negotiate capabilities |
ping |
PingRequestSchema |
Health check |
tools/list |
ListToolsRequestSchema |
Discover available tools |
tools/call |
CallToolRequestSchema |
Execute a tool |
resources/list |
ListResourcesRequestSchema |
Discover available resources |
resources/read |
ReadResourceRequestSchema |
Read resource content |
resources/subscribe |
SubscribeRequestSchema |
Subscribe to resource updates |
resources/unsubscribe |
UnsubscribeRequestSchema |
Cancel subscription |
resources/templates/list |
ListResourceTemplatesRequestSchema |
List resource templates |
prompts/list |
ListPromptsRequestSchema |
Discover available prompts |
prompts/get |
GetPromptRequestSchema |
Get prompt details |
logging/setLevel |
SetLevelRequestSchema |
Configure logging verbosity |
roots/list |
ListRootsRequestSchema |
List filesystem roots |
Server → Client Requests
| Method | Schema Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
ping |
PingRequestSchema |
Server-initiated health check |
sampling/createMessage |
CreateMessageRequestSchema |
Request message creation from LLM |
elicitation/create |
ElicitRequestSchema |
Request user input |
completion/complete |
CompleteRequestSchema |
Request text completion |
Notifications (No Response Expected)
| Method | Schema Type | Direction | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
initialized |
InitializedNotificationSchema |
Client → Server | Confirm initialization complete |
cancelled |
CancelledNotificationSchema |
Both directions | Cancel in-progress operation |
progress |
ProgressNotificationSchema |
Both directions | Report operation progress |
resources/updated |
ResourceUpdatedNotificationSchema |
Server → Client | Resource content changed |
resources/list_changed |
ResourceListChangedNotificationSchema |
Server → Client | Available resources changed |
prompts/list_changed |
PromptListChangedNotificationSchema |
Server → Client | Available prompts changed |
tools/list_changed |
ToolListChangedNotificationSchema |
Server → Client | Available tools changed |
logging/message |
LoggingMessageNotificationSchema |
Server → Client | Log output |
roots/list_changed |
RootsListChangedNotificationSchema |
Server → Client | Filesystem roots changed |
MCP JSON-RPC Message Structure
Every MCP message follows the JSON-RPC 2.0 specification. There are three fundamental message types:
1. MCP Request (Expects Response)
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "unique-id-123",
"method": "tools/list",
"params": {}
}
2. MCP Response (Reply to Request)
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": "unique-id-123",
"result": {
"tools": [...]
}
}
3. MCP Notification (Fire and Forget)
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "progress",
"params": {
"progress": 50,
"total": 100
}
}
Note: Notifications have no id field and don't receive responses.
Understanding Capabilities
Capabilities are the heart of MCP's flexibility. During initialization, both client and server advertise what they can do, creating a contract for their interaction. This prevents runtime errors and enables graceful degradation when features aren't available.
How Capability Negotiation Works
- MCP Client announces what it can handle (initialize request)
- MCP Server responds with what it offers (initialize response)
- Both parties only use mutually supported features
- Runtime errors are avoided through upfront negotiation
Client Capabilities
MCP Clients advertise what server features they can handle:
{
"capabilities": {
"roots": {
"listChanged": true // Can handle roots/list_changed notifications
},
"sampling": {
// Supports sampling/createMessage requests from server
},
"experimental": {
// Optional: Custom capabilities for extensions
"customFeature": true
}
}
}
Important: If a client doesn't advertise a capability, the server must not use that feature. For example, if sampling is missing, the server cannot send sampling/createMessage requests.
Server Capabilities
MCP Servers advertise what features they provide:
{
"capabilities": {
"tools": {
// Server provides tools (empty object means basic support)
},
"resources": {
"subscribe": true, // Supports resource subscriptions
"listChanged": true // Will send resources/list_changed notifications
},
"prompts": {
"listChanged": true // Will send prompts/list_changed notifications
},
"logging": {
// Supports logging/setLevel and will send logging/message
}
}
}
Capability Rules
- No capability = No feature: If not advertised, assume unavailable
- Empty object = Basic support:
"tools": {}means tools are available but without special features - Nested properties = Specific features:
"resources": { "subscribe": true }means resources with subscription support - Check before use: Always verify capability exists before using a feature
Common Capability Patterns
Basic Server (Minimal Capabilities)
{
"capabilities": {
"tools": {} // Only provides tools, nothing else
}
}
Full-Featured Server
{
"capabilities": {
"tools": {
"listChanged": true // Dynamic tool registration
},
"resources": {
"subscribe": true, // Resource subscriptions
"listChanged": true // Dynamic resource list
},
"prompts": {
"listChanged": true // Dynamic prompt templates
},
"logging": {} // Logging support
}
}
Advanced Client
{
"capabilities": {
"roots": {
"listChanged": true // Handle filesystem changes
},
"sampling": {}, // Can provide LLM sampling
"experimental": {
"debugging": true, // Custom debugging features
"metrics": true // Performance metrics
}
}
}
Capability-Dependent Message Flow
Here's how capabilities affect which messages can be sent:
| Server Capability | Enables Server Messages | Required for Client Messages |
|---|---|---|
tools |
- | tools/list, tools/call |
tools.listChanged |
tools/list_changed notification |
- |
resources |
- | resources/list, resources/read |
resources.subscribe |
resources/updated notification |
resources/subscribe, resources/unsubscribe |
resources.listChanged |
resources/list_changed notification |
- |
prompts |
- | prompts/list, prompts/get |
prompts.listChanged |
prompts/list_changed notification |
- |
logging |
logging/message notification |
logging/setLevel |
| Client Capability | Enables Client Messages | Required for Server Messages |
|---|---|---|
roots |
roots/list |
- |
roots.listChanged |
- | roots/list_changed notification |
sampling |
- | sampling/createMessage, completion/complete |
Implementation Example: Checking Capabilities
class MCPClient {
constructor() {
this.serverCapabilities = null;
}
async connect(transport) {
// Send initialize request
const response = await this.sendRequest({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: 1,
method: "initialize",
params: {
protocolVersion: "2024-11-05",
capabilities: {
sampling: {}, // We support sampling
roots: {
listChanged: true // We can handle root changes
}
},
clientInfo: {
name: "my-client",
version: "1.0.0"
}
}
});
// Store server capabilities
this.serverCapabilities = response.result.capabilities;
// Send initialized notification
await this.sendNotification({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
method: "initialized"
});
}
async subscribeToResource(uri) {
// Check capability before using feature
if (!this.serverCapabilities?.resources?.subscribe) {
throw new Error("Server doesn't support resource subscriptions");
}
return await this.sendRequest({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: this.nextId(),
method: "resources/subscribe",
params: { uri }
});
}
async callTool(name, arguments) {
// Check if server provides tools at all
if (!this.serverCapabilities?.tools) {
throw new Error("Server doesn't provide tools");
}
return await this.sendRequest({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: this.nextId(),
method: "tools/call",
params: { name, arguments }
});
}
}
MCP Server Implementation: Advertising Capabilities
class MCPServer {
constructor() {
// Define what this server can do
this.capabilities = {
tools: {}, // We provide tools
resources: {
subscribe: true, // We support subscriptions
listChanged: true // We'll notify about resource changes
}
};
this.clientCapabilities = null;
}
async handleInitialize(params) {
// Store what the client can do
this.clientCapabilities = params.capabilities;
// Return our capabilities
return {
protocolVersion: "2024-11-05",
capabilities: this.capabilities,
serverInfo: {
name: "my-server",
version: "1.0.0"
}
};
}
async requestSampling(messages) {
// Check if client supports sampling before requesting
if (!this.clientCapabilities?.sampling) {
throw new Error("Client doesn't support sampling");
}
return await this.sendRequest({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: this.nextId(),
method: "sampling/createMessage",
params: { messages }
});
}
async notifyResourcesChanged() {
// Only send if we advertised this capability
// AND client can handle it
if (!this.capabilities.resources?.listChanged) {
return; // We didn't advertise this
}
// Note: For notifications, client doesn't need to advertise support
// They just ignore notifications they don't understand
await this.sendNotification({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
method: "resources/list_changed"
});
}
}
Common Capability Mistakes
- Using boolean at top level:
// ❌ Bad: Top-level capabilities should be objects
{
capabilities: {
tools: true, // WRONG!
resources: true // WRONG!
}
}
// ✅ Good: Use empty object for basic support
{
capabilities: {
tools: {},
resources: {}
}
}
- Not checking sub-features:
// ❌ Bad: Assumes subscription support just because resources exist
if (serverCapabilities.resources) {
await client.request("resources/subscribe", { uri: "file.txt" });
}
// ✅ Good: Checks specific sub-capability
if (serverCapabilities.resources?.subscribe) {
await client.request("resources/subscribe", { uri: "file.txt" });
}
- Forgetting to advertise capabilities:
// ❌ Bad: Server implements features but doesn't advertise them
{
capabilities: {} // Empty - client won't know about any features!
}
// ✅ Good: Explicitly advertises what's available
{
capabilities: {
tools: {},
resources: { subscribe: true },
prompts: {}
}
}
- Sending notifications without advertising:
// ❌ Bad: Sends notification without advertising capability
async notifyToolsChanged() {
await this.send({ method: "tools/list_changed" });
}
// ✅ Good: Only sends if advertised (though clients should ignore unknown notifications)
async notifyToolsChanged() {
if (this.capabilities.tools?.listChanged) {
await this.send({ method: "tools/list_changed" });
}
}
Lifecycle Messages
Initialize Request
The first message in any MCP session. The client announces its capabilities and protocol version.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "initialize",
"params": {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
"capabilities": {
"roots": {
"listChanged": true
},
"sampling": {}
},
"clientInfo": {
"name": "Claude Desktop",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"result": {
"protocolVersion": "2024-11-05",
"capabilities": {
"tools": {},
"resources": {
"subscribe": true
}
},
"serverInfo": {
"name": "example-server",
"version": "1.0.0"
}
}
}
Initialized Notification
Client confirms initialization is complete. Server can now start sending notifications.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "initialized"
}
Ping Request
Keep-alive and health check mechanism. Both client and server can initiate.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "ping"
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"result": {}
}
Tool Messages
List Tools Request
Discover what tools the server provides.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"method": "tools/list"
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 3,
"result": {
"tools": [
{
"name": "calculate",
"description": "Perform basic math operations",
"inputSchema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"operation": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]
},
"a": {"type": "number"},
"b": {"type": "number"}
},
"required": ["operation", "a", "b"]
}
}
]
}
}
Call Tool Request
Execute a tool with arguments.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 4,
"method": "tools/call",
"params": {
"name": "calculate",
"arguments": {
"operation": "multiply",
"a": 7,
"b": 6
}
}
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 4,
"result": {
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "The result is 42"
}
]
}
}
Tools List Changed Notification
Server notifies client that available tools have changed.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "tools/list_changed"
}
Resource Messages
List Resources Request
Discover available data sources.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 5,
"method": "resources/list"
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 5,
"result": {
"resources": [
{
"uri": "file:///config.json",
"name": "Configuration",
"description": "Application configuration file",
"mimeType": "application/json"
}
]
}
}
Read Resource Request
Retrieve resource content.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 6,
"method": "resources/read",
"params": {
"uri": "file:///config.json"
}
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 6,
"result": {
"contents": [
{
"uri": "file:///config.json",
"mimeType": "application/json",
"text": "{\"debug\": true, \"port\": 3000}"
}
]
}
}
Subscribe to Resource Request
Watch for changes to a resource.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 7,
"method": "resources/subscribe",
"params": {
"uri": "file:///logs/app.log"
}
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 7,
"result": {}
}
Resource Updated Notification
Server notifies about resource changes (after subscription).
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "resources/updated",
"params": {
"uri": "file:///logs/app.log"
}
}
Unsubscribe Request
Stop watching a resource.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 8,
"method": "resources/unsubscribe",
"params": {
"uri": "file:///logs/app.log"
}
}
Prompt Messages
List Prompts Request
Discover available prompt templates.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 9,
"method": "prompts/list"
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 9,
"result": {
"prompts": [
{
"name": "code-review",
"description": "Generate a code review for the given code",
"arguments": [
{
"name": "code",
"description": "The code to review",
"required": true
}
]
}
]
}
}
Get Prompt Request
Retrieve a prompt template with arguments filled in.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 10,
"method": "prompts/get",
"params": {
"name": "code-review",
"arguments": {
"code": "function add(a, b) { return a + b; }"
}
}
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 10,
"result": {
"description": "Code review for the provided function",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "Please review this code:\n\nfunction add(a, b) { return a + b; }"
}
}
]
}
}
Sampling Messages (Server → Client)
These allow servers to request LLM capabilities from the client.
Create Message Request
Server asks client to generate an LLM response in this JSON-RPC format request.
Request (from server):
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 11,
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "What is the capital of France?"
}
}
],
"maxTokens": 100
}
}
Response (from client):
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 11,
"result": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "The capital of France is Paris."
}
}
}
Logging Messages
Set Log Level Request
Configure server logging verbosity.
Request:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 12,
"method": "logging/setLevel",
"params": {
"level": "debug"
}
}
Response:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 12,
"result": {}
}
Logging Message Notification
Server sends log output to client.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "logging/message",
"params": {
"level": "info",
"logger": "server",
"data": "Tool 'calculate' executed successfully",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"
}
}
Error Handling
When requests fail, servers return error responses following JSON-RPC error format:
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 13,
"error": {
"code": -32601,
"message": "Method not found",
"data": {
"method": "unknown/method"
}
}
}
Standard MCP Error Codes
| Code | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -32700 | Parse error | Invalid JSON |
| -32600 | Invalid request | Not a valid JSON-RPC request |
| -32601 | Method not found | Unknown method |
| -32602 | Invalid params | Invalid method parameters |
| -32603 | Internal error | Internal server error |
| -32000 to -32099 | Server error | MCP-specific errors |
Progress Notifications
Both client and server can send progress updates for long-running operations.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "progress",
"params": {
"progressToken": "operation-123",
"progress": 75,
"total": 100,
"message": "Processing files..."
}
}
Cancellation
Either party can cancel an in-progress operation.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "cancelled",
"params": {
"requestId": "long-running-request-id",
"reason": "User requested cancellation"
}
}
TypeScript Implementation
All these types are available in the official MCP SDK:
import {
ClientRequestSchema,
ServerRequestSchema,
ClientNotificationSchema,
ServerNotificationSchema,
InitializeRequestSchema,
CallToolRequestSchema,
// ... other types
} from '@modelcontextprotocol/sdk/types';
// Example: Type-safe request handling
function handleRequest(message: ClientRequestSchema) {
switch (message.method) {
case 'initialize':
return handleInitialize(message.params);
case 'tools/call':
return handleToolCall(message.params);
// ... handle other methods
}
}
Common Implementation Patterns
1. Message Correlation
Always preserve the id field when responding to requests:
async function handleMessage(message) {
if (message.id !== undefined) {
try {
const result = await processRequest(message);
return {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: message.id, // Critical: use same ID
result
};
} catch (error) {
return {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: message.id, // Include ID even in errors
error: {
code: -32603,
message: error.message
}
};
}
}
// Handle notification (no response needed)
await processNotification(message);
}
2. Capability Negotiation
Always check server capabilities before using features:
const initResponse = await sendRequest({
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: 1,
method: "initialize",
params: { /* ... */ }
});
const hasSubscriptions = initResponse.result.capabilities.resources?.subscribe;
if (hasSubscriptions) {
// Safe to use subscribe/unsubscribe
}
3. Batch Requests
JSON-RPC supports sending multiple requests together:
[
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 1,
"method": "tools/list"
},
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"id": 2,
"method": "resources/list"
}
]
Debugging Tips
- Missing
idin response: Most issues are malformed MCP JSON-RPC messages: missingidor version mismatch. Ensure you're copying the request ID to the response - No response to notification: Notifications (no
idfield) should not receive responses - Method not found errors: Check the exact method string including namespace (e.g.,
tools/listnot justlist) - Protocol version mismatch: Always send
protocolVersionin initialize request - Capability not available: Server didn't advertise the capability during initialization
Next Steps
Now that you understand MCP message types:
- Build an MCP Server: Use this reference to implement each message handler
- Debug Connections: Use the examples to verify correct message format
- Extend the Protocol: MCP allows custom methods with the same JSON-RPC structure
For a complete working example, check out our MCP server implementation on GitHub.
This guide covers the MCP specification as of protocol version 2024-11-05. For the latest updates, refer to the official MCP documentation.