⭐ Semantic Cache for Large Language Models
Learn how semantic caching for large language models reduces cost, improves latency, and stabilizes high-volume AI applications by reusing responses based on intent, not just text.

LLM spend is rising across every industry. As teams move from prototypes to real usage, they quickly realise that even “cheap” models become expensive at scale. A few cents per request looks manageable in isolation — but when a customer-facing application handles millions of queries each month, those cents stack up fast.
And it’s not just cost. High-traffic workloads also amplify latency, throughput, and reliability challenges. Each request triggers a fresh call to a large model, even when users are asking questions with the same underlying intent.
As organizations push to control LLM costs without compromising quality, semantic caching in LLMs is becoming one of the most effective optimizations for production-scale AI systems.
Semantic caching in LLMs: what it is and how it works
Semantic cache considers the contextual similarity between input requests. It uses cosine similarity to see if the similarity between the input and a cached request exceeds a specific threshold. If the similarity threshold is met, the response is retrieved from cache, saving model execution time.
Traditional caching only works when two prompts match exactly, a rare occurrence in real applications.
Latency and Cost are significant hurdles for developers building on top of popular Large Language Models. High latency can degrade the user experience, and increased costs can impact scalability.
Semantic Cache efficiently addresses these challenges. Early tests for Portkey's semantic cache reveal a promising ~20% cache hit rate at 99% accuracy for Q&A (or RAG) use cases.
Picture this: You've built a popular AI application, and you're processing a lot of LLM API calls daily. You notice that users often ask similar questions - questions you've already answered before. However, with each call to the LLM, you incur costs for all those redundant tokens, and your users have a sub-par experience.
This is where Semantic Cache comes into play. It allows you to serve a cached response for semantically repeated queries instead of resorting to your AI provider, saving you costs and reducing latency.

To illustrate the extent of semantic similarity covered and the time saved, we ran a simple query, changing it a little each time and noting down the time.

Despite variations in the question, Portkey's semantic cache identified the core query each time and provided the answer in a fraction of the initial time.
We also ran the same test on a set of queries that may look similar but require different responses.

While this is a promising start, we are committed to enhancing cache performance further and expanding the breadth of semantic similarity we can cover.
In Q&A scenarios like enterprise search & customer support, we discovered that over 20% of the queries were semantically similar. With Semantic Cache, these requests can be served without the typical inference latency & token cost, offering a potential speed boost of at least 20x at zero cost to you.
📈 Impact of Caching
Let's look at the numbers. Despite recent improvements in GPT 3.5's response times through Portkey, it's evident that cached responses via our edge infrastructure are considerably quicker.
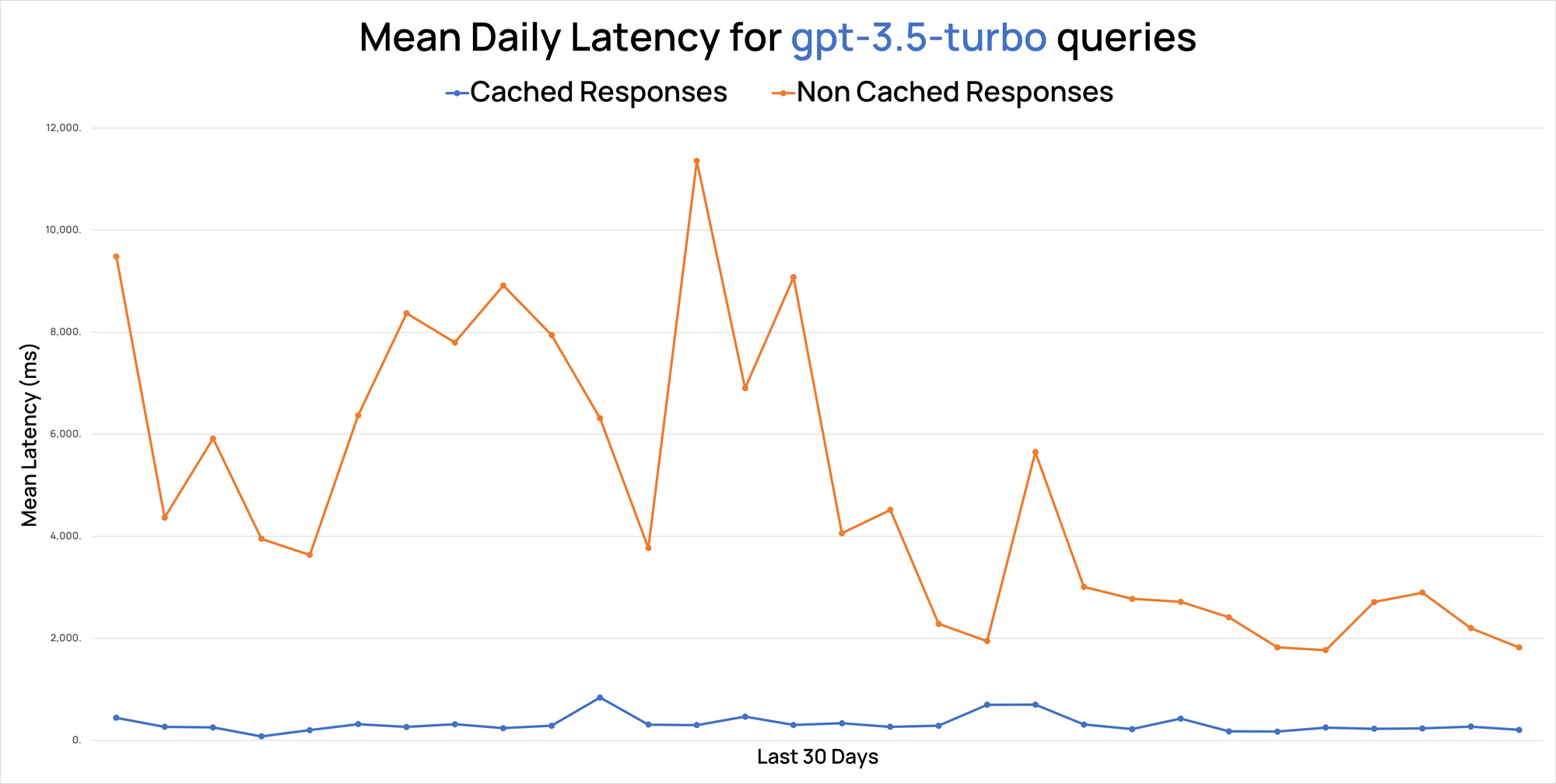
In RAG use cases, we observed a cache hit rate ranging between 18% to as high as 60%, delivering accurate results 99% of the time.
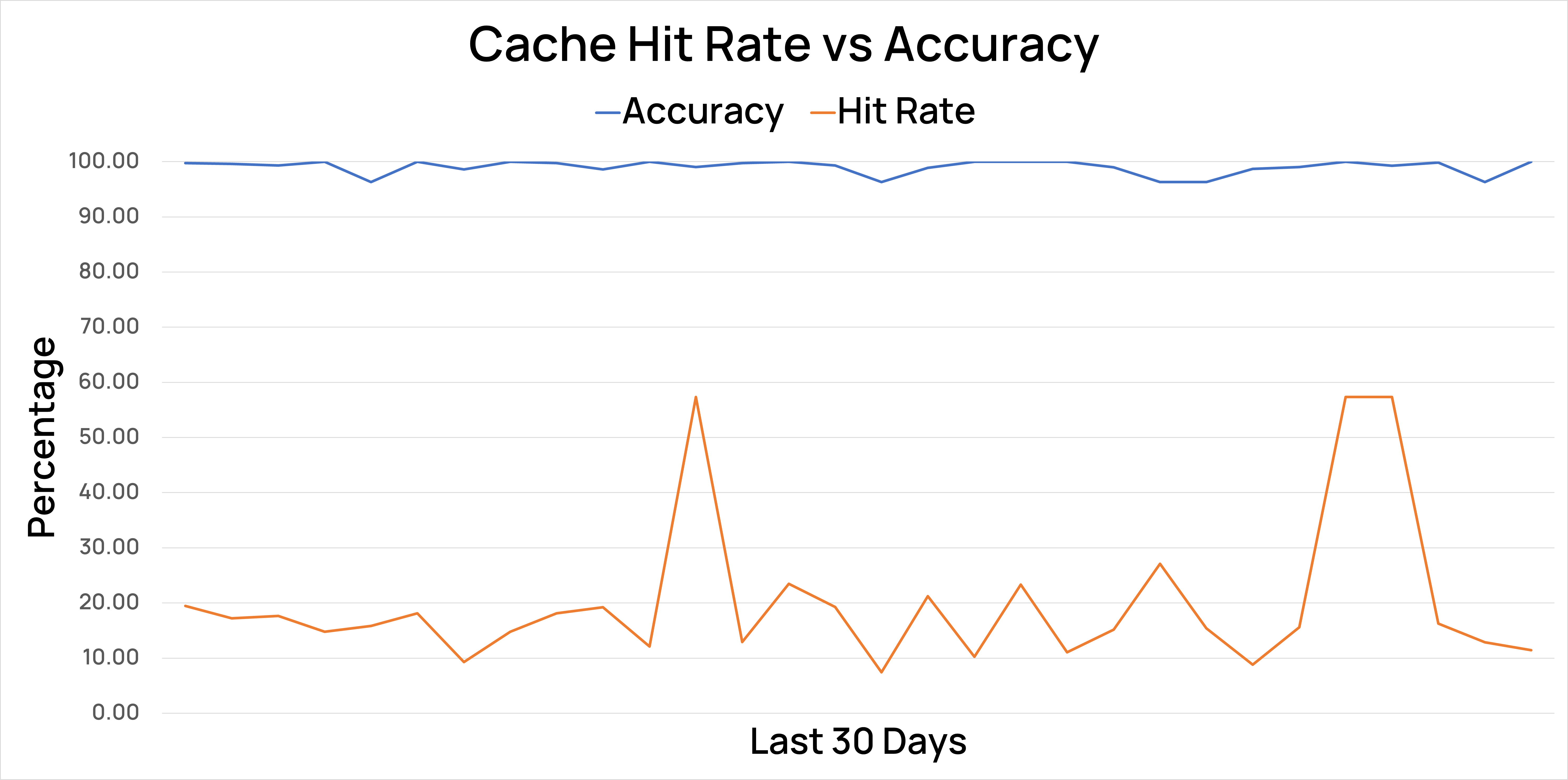
🧮 Evaluating Cache Effectiveness
Semantic Cache's effectiveness can be evaluated by checking how many similar queries you get over a specified period - that's your expected cache hit rate.
You can use a model-graded eval to test the semantic match's accuracy at various similarity thresholds. We’d recommend starting with a 95% confidence and then tweaking it to ensure your accuracy is high enough to perform a cache call.
Here's a simple tool that calculates the money saved on GPT4 calls based on the expected cache hit rate.
Click on Run Pen to start:
🎯 Our Approach To Semantic Cache
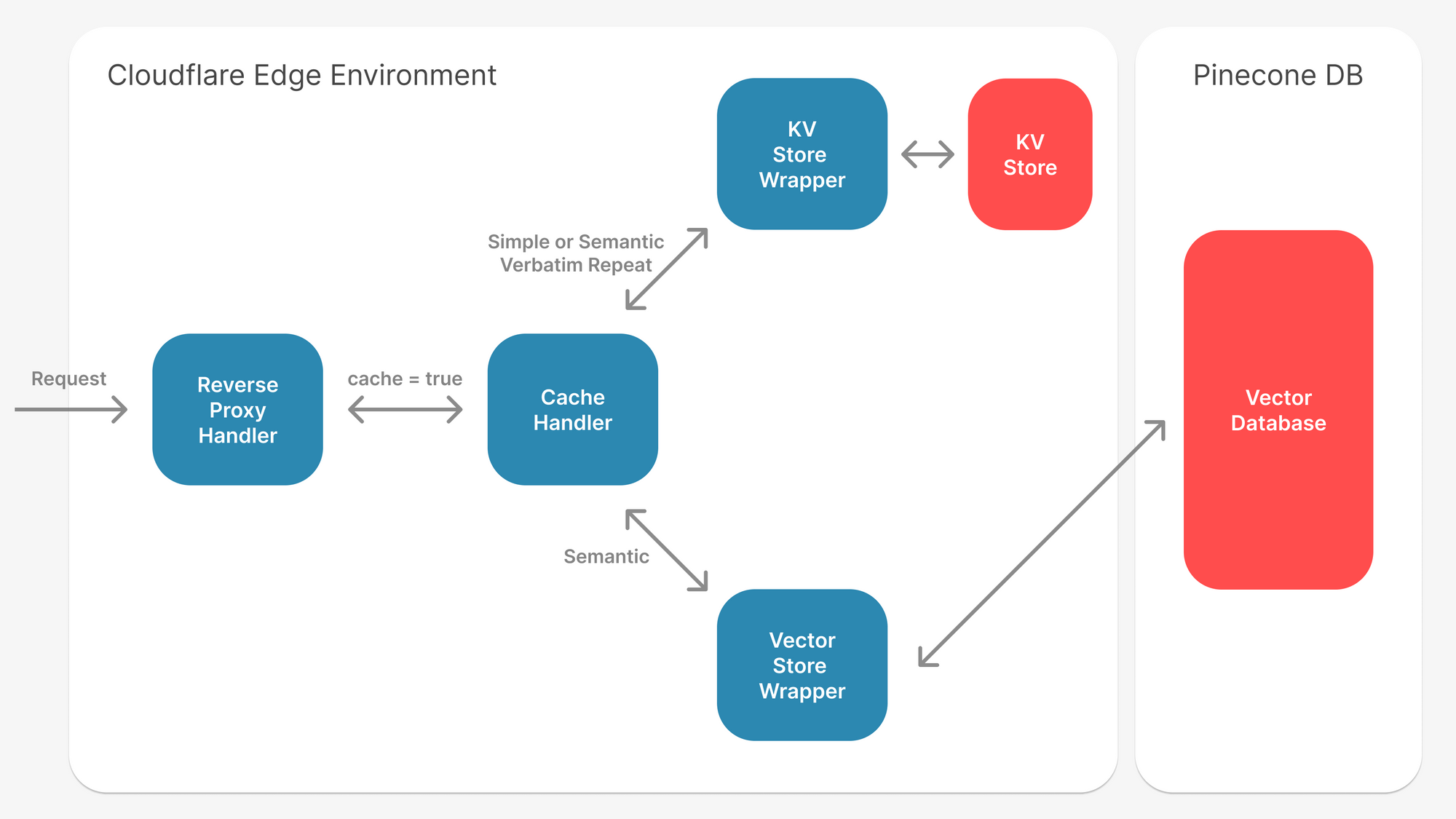
First, we check for exact repeat queries, leveraging Cloudflare’s key-value store for quick and efficient responses.
For unique queries, we apply a vector search on Pinecone, enhanced with a hybrid search that utilizes meta properties inferred from inputs. We also preprocess inputs to remove redundant content, which improves the accuracy of the vector search.
To ensure top-notch results, we run backtests to adjust the vector confidence individually for each customer.
When semantic caching for LLMs works well
Semantic caching delivers the most value in environments where users generate large volumes of queries that circle around the same themes, intents, or problem patterns. These patterns appear far more often than teams expect especially once LLM-powered applications reach production scale.
High-volume customer-facing applications
Support bots, helpdesk assistants, and product Q&A systems receive thousands of variations of the same questions every day.
Even when wording differs — “I can’t log in,” “login not working,” “stuck at signin” — the underlying intent is identical. A semantic cache can capture a large percentage of such traffic and return instant answers.
Internal knowledge assistants
Employees frequently ask similar procedural and policy questions. Because internal knowledge evolves slowly, cached responses remain accurate for longer periods, making caching highly efficient.
Coding assistants and developer tools
Engineers repeatedly search for patterns like error explanations, dependency issues, refactoring tips, or boilerplate code. These patterns are stable, and caching them avoids unnecessary LLM calls for common scenarios.
Agentic workflows
Agents often repeat sub-tasks across many runs summarizing, classifying, routing, extracting, explaining. Semantic caching prevents agents from hitting the LLM for identical micro-steps each time.
Any workload with predictable or clustered user intent
Chat interfaces, onboarding flows, knowledge retrieval systems, and domain-specific copilots all show repeated semantic structures at scale.
In these environments, a well-tuned semantic cache can reduce LLM calls significantly while improving user-perceived speed.
Benefits of semantic caching for LLM-heavy systems
Lower LLM spend, especially at scale
For applications serving millions of queries, even a modest cache hit rate translates into substantial cost savings. Every avoided LLM call is direct budget relief — no tokens, no compute, no provider charges.
Faster response times for end-users
Cached responses are served instantly. This matters most in customer-facing applications, where latency directly impacts satisfaction and engagement. A semantic cache can shave hundreds of milliseconds (or more) off every hit.
More predictable performance under load
Heavy traffic normally stresses LLM APIs and routing systems. With a semantic cache absorbing repetitive requests, overall throughput stabilizes. Fewer LLM calls also reduce the risk of rate limits, provider outages, and sudden latency spikes.
Higher throughput for the same infrastructure
Teams can handle more concurrent users without scaling up compute or capacity. This is particularly valuable for real-time assistants, live agent workflows, and enterprise-wide deployments.
Reduced dependency on model choice for repeated queries
When several providers offer similar capabilities, semantic caching avoids recalculating the same output across models. It also helps neutralize cost differences across vendors by reusing work already done.
Improved UX consistency
For tasks where users expect stable answers semantic caching ensures responses remain consistent, even if underlying models change or evolve.
In multi-provider LLM setups, semantic caching acts as a unifying layer that cuts down duplicate work across models.
Instead of recalculating similar prompts on different providers, a shared semantic cache lets the system reuse past responses regardless of which model originally produced them. This reduces overall spend, keeps behaviour consistent across heterogeneous providers, and helps applications remain stable during provider-specific slowdowns or outages.
By sitting above routing logic, semantic caching ensures teams don’t pay multiple times for the same underlying intent, a meaningful advantage in architectures where traffic is distributed across OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Bedrock, and others.
Challenges of using Semantic Cache
Semantic Cache, while efficient, does have some challenges.
For instance, while a regular cache operates at 100% accuracy, a semantic cache can sometimes be incorrect. Embedding the entire prompt for the cache can also sometimes result in lower accuracy.
- We built our cache solution on top of OpenAI embeddings & Pinecone's vector search. We combine it with advanced text manipulation & hybrid search inferred from metadata to remove irrelevant parts of the prompt.
- We only return a cache hit if there is >95% confidence in similarity.
- In our tests, users rated the semantic cache accuracy at 99%.
Additionally, improper management could potentially lead to data and prompt leakage.
- We encrypt the whole request with
SHA256and run our cache system on top of it to prevent containment. - Each organization's data, prompts, and responses are encrypted and secured under different namespaces to ensure security.
- Additional metadata stored as part of the vector also mitigates leakage risks.
How to Use Semantic Cache on Portkey
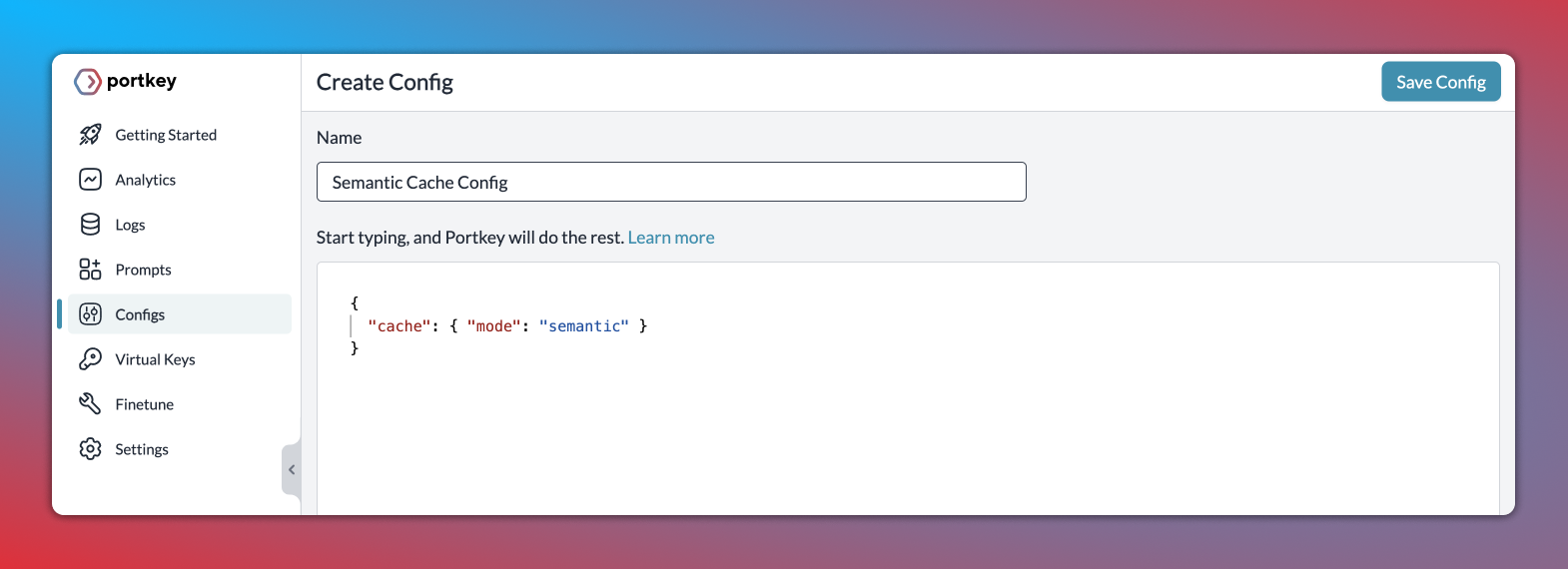
Step 1: Enable semantic cache in Portkey's Config object
Just set the cache mode as semantic and save the Config↓
{
"cache": { "mode": "semantic" }
}
Step 2: Pass the Config ID while making your request
In the Portkey SDK, you can pass the config ID while instantiating the client and then make your request just as you would usually:
from portkey_ai import Portkey
portkey = Portkey(
api_key="PORTKEY_API_KEY",
virtual_key="openai-xxx",
config="pp-semantic-cache"
)
response = portkey.chat.completions.create(
messages = [{ "role": 'user', "content": 'Portkey's semantic cache saves time and money' }],
model = 'gpt-4'
)Refresh your cache
You can clear any previously stored cache value and fetch a new value using this feature. In the SDK, just set the cache_force_refresh flag at True ↓
response = portkey.with_options(
cache_force_refresh = True
).chat.completions.create(
messages = [{ "role": 'user', "content": 'Hello!' }],
model = 'gpt-4'
)
Check out Portkey docs for detailed instructions on how to use semantic cache.
Semantic caching is one of the most effective techniques for improving the efficiency of LLM applications. By recognizing repeated intent instead of just repeated text, it reduces cost, improves latency, and stabilizes performance for high-volume workloads. As organizations scale their AI deployments, adding a semantic cache layer becomes a straightforward way to create fast, predictable, and cost-efficient systems.
If you want to implement semantic caching across all your LLM providers with no infrastructure work, you can try it directly through Portkey’s AI Gateway or book a demo with the team.
PS: Portkey hosted the Chief Architect of Walmart to discuss how Walmart is doing semantic caching at scale and the conversation was enlightening! You can watch it here: